Part II
Governmental Powers
- 12. Limiting Powers: EU Fundamental Rights
- 1. Constitutional History: From Paris To Lisbon
- 13. Free Movement: Goods I—Negative Integration
- 2. Constitutional Nature: A Federation Of States
- 14. Free Movement: Goods II—Positive Integration
- 15. Free Movement: Persons—Workers and Beyond
- 16. Free Movement: Services and Capital
- 3. Governmental Structure: Union Institutions I
- 17. EU Competition Law: Private Undertakings
- 18. EU Internal Policies: An Overview
- 4. Governmental Structure: Union Institutions II
- 19. EU External Policies: An Overview
- 20. Epilogue: Brexit and the Union: Past, Present, Future
- 5. European Law I: Nature—Direct Effect
- 21. Appendix: How to Study European Law
- 7. Legislative Powers: Competence and Procedures
- 8. External Powers: Competence and Procedures
- 6. European Law II: Nature—Primacy/Pre-emption
- 9. Executive Powers: Competence and Procedures
- 10. Judicial Powers I: (Centralized) European Procedures
- 11. Judicial Powers II: (Decentralized) National Procedures
- 22. Extra chapter: Competition Law II: State Interferences
Introduction
The protection of human rights is a central task of many judiciaries. Judicial review in light of fundamental human rights may here be limited to the review of the executive; yet in its expansive form, it includes the judicial review of legislative acts. The European Union follows this second tradition. Fundamental rights set substantive – judicial – limits to all governmental powers and processes within the Union. They indeed constitute one of the most popular grounds of judicial review in actions challenging the validity of European Union law.
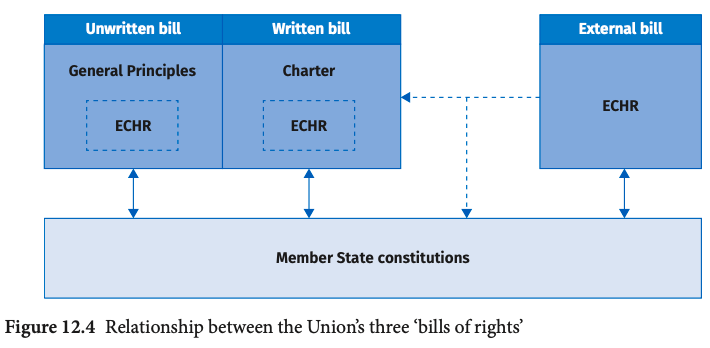
What are the sources of human rights in the Union legal order? Despite the absence of a ‘bill of rights’ in the original Treaties, three sources for EU fundamental rights were subsequently developed. The European Court first began distilling fundamental rights from the constitutional traditions of the Member States. This unwritten bill of rights was inspired and informed by a second bill of rights: the European Convention on Human Rights. This external bill of rights was subsequently matched by a – third – written bill of rights specifically drafted for the European Union: the EU Charter of Fundamental Rights. These three sources of EU fundamental rights are now expressly referred to – in reverse order – in Article 6 of the Treaty on European Union. The provision reads:
1. The Union recognises the rights, freedoms and principles set out in the Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union of 7 December 2000, as adopted at Strasbourg, on 12 December 2007, which shall have the same legal value as the Treaties …
2. The Union shall accede to the European Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms. Such accession shall not affect the Union’s competences as defined in the Treaties.
3. Fundamental rights, as guaranteed by the European Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms and as they result from the constitutional traditions common to the Member States, shall constitute general principles of the Union’s law.
This chapter investigates each of the Union’s three bills of rights and the constitutional principles that govern them. Section 1 starts with the discovery of an ‘unwritten’ bill of rights in the form of general principles of European law. Section 2 then moves to an analysis of the Union’s ‘written’ bill of rights: the EU Charter of Fundamental Rights, which was adopted to codify existing human rights in the Union legal order. Section 3 investigates the formal relationship between the Union and the European Convention on Human Rights. Finally, section 4 explores the relationship between all three bills of rights and the Member States. It will be seen that each of the three Union bills applies, at least to some extent, also to the Member States. National courts may thus be obliged to review the legality of national law also in light of EU fundamental rights.

Cases
Legislation
EU Directives
Council Regulation (EEC) No. 990/93 of 26 April 1993 concerning trade between the European Economic Community and the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (Serbia and Montenegro) [1993] OJ L 102/14
Council Regulation (EC) No. 881/2002 of 27 May 2002 imposing certain specific restrictive measures directed against certain persons and entities associated with Usama bin Laden, the Al-Qaida network and the Taliban, and repealing Council Regulation (EC) No. 467/2001 prohibiting the export of certain goods and services to Afghanistan, strengthening the flight ban and extending the freeze of funds and other financial resources in respect of the Taliban of Afghanistan, [2002] OJ L 139/9
Council Regulation (EC) No. 1290/2005 of 21 June 2005 on the financing of the common agricultural policy, [2005] OJ L 209/1
Commission Regulation (EC) No. 259/2008 of 18 March 2008 laying down detailed rules for the application of Council Regulation (EC) No. 1290/2005 as regards the publication of information on the beneficiaries of funds deriving from the European Agricultural Guarantee Fund (EAGF) and the European Agricultural Fund for Rural Development (EAFRD), [2008] OJ L 76/28
EU Directives
EU Decisions
Figures

Extra Materials
Useful Videos
Useful websites
Further Reading
Books
P. Alston (ed.), The EU and Human Rights (Oxford University Press, 1999)
E. Frantziou, The Horizontal Effect of Fundamental Rights in the European Union: A Constitutional Analysis (Oxford University Press, 2019)
S. Morano-Foadi and L. Vickers, Fundamental Rights in the EU: A Matter of Two Courts (Hart, 2017)
S. Peers et al., The EU Charter of Fundamental Rights: A Commentary (Hart, 2014)
T. Tridimas, The General Principles of EU Law (Oxford University Press, 2007)
S. de Vries et al. (eds), The Protection of Fundamental Rights in the EU After Lisbon (Hart, 2013)
S. de Vries et al. (eds), The EU Charter of Fundamental Rights as a Binding Instrument (Hart, 2015)
A. Williams, EU Human Rights Policies: A Study in Irony (Oxford University Press, 2004)
J. Wouters and M. Ovádek, The European Union and Human Rights: Analysis, Cases, and Materials (Oxford University Press, 2021)
Articles
G. de Búrca, ‘The Evolution of EU Human Rights Law’ in P. Craig and G. de Búrca (eds.), The Evolution of EU Law (Oxford University Press, 2011), 465
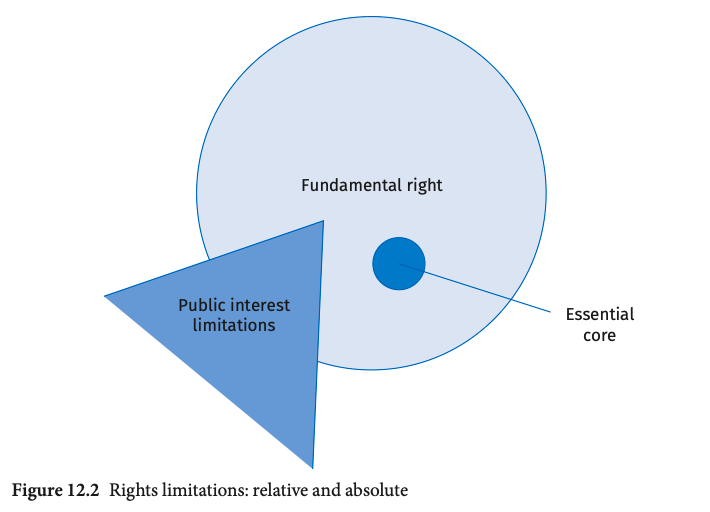
F. de Cecco ‘The Trouble with Trumps: On How (and Why) Not to Define the Core of Fundamental Rights’ (2023) 60 CML Rev. 1551
J. Coppel and A. O’Neill, ‘The European Court of Justice: Taking Rights Seriously?’ (1992) 29 CML Rev 669
S. Douglas-Scott, ‘A Tale of Two Courts: Luxembourg, Strasbourg and the Growing European Human Rights Acquis’ (2006) 43 CML Rev 629
E. Hancox, ‘The Relationship between the Charter and General Principles: Looking Back and Looking Forward’ (2020) 22 Cambridge Yearbook of European Legal Studies 233.
J. Krommendijk, ‘Principled Silence or Mere Silence on Principles? The Role of the EU Charter’s Principles in the Case Law of the Court of Justice’ (2015) 11 European Constitutional Law Review 321
K. Lenaerts, ‘Limits on Limitations: The Essence of Fundamental Rights in the EU’ (2019) 20 German Law Journal 779
T. Lock, ‘End of an Epic? The Draft Agreement on the EU’s Accession to the ECHR’ (2012) 31 YEL 162
J. Weiler, ‘Does the European Union Truly Need a Charter of Rights’ (2000) 6 ELJ 95
How to Find (and Read) the EU Treaties
The EU Treaties constitute the primary law of the Union. The formula the ‘EU Treaties’ or simply ‘the Treaties’ commonly refers to two Treaties: the Treaty on European Union (TEU) and the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union (TFEU).
The ‘Treaties’ are the result of a long ‘chain novel’ of consecutive treaties (see Table 20.1). They started out from three ‘Founding Treaties’ that created the European Coal and Steel Community (1951), the European Atomic Energy Community (1957) and the European (Economic) Community (1957). A myriad of subsequent ‘Amendment Treaties’ and ‘Accession Treaties’ gradually changed the textual basis of the three Communities significantly; and this first treaty base would be complemented by a second treaty base in 1992, when the Maastricht Treaty created the (old) European Union.
To simplify the – very complex – textual foundations of the old European Union and European Communities Treaties, the Member States tried to create a single treaty in the early 2000s. The 2004 Constitutional Treaty was indeed intended to repeal all previous treaties; and it was to merge the European Union with the European Communities. Yet the attempt to ‘recreate’ one Union, with one legal personality, on the basis of one treaty failed; and the Member States thereafter resorted to yet another ‘Amendment Treaty’: the 2007 Reform Treaty – also called the Lisbon Treaty.
Despite its modest name, the Lisbon Treaty constitutes a radical new ‘chapter’ in the Union’s constitutional chain novel. For while it formally builds on the original ‘Founding Treaties’, it has nonetheless ‘merged’ the old ‘Community’ legal order with the old ‘Union’ legal order into a new ‘Union’ legal order.



Nevertheless, unlike the 2004 Constitutional Treaty, the 2007 Lisbon Treaty has not created a single treaty base for the European Union. Instead, it recognises the existence of two (main) treaties: the Treaty on European Union and the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union. The division into two EU Treaties thereby follows a functional criterion: the Treaty on European Union (TEU) contains the general provisions defining the Union, while the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union (TFEU) contains the specific provisions with regard to the Union institutions and policies. One of the new features of the post-Lisbon era is the possibility of minor treaty amendments instigated by European Council Decisions.

In addition to ‘Amendment Treaties’ there are now also ‘Amendment Decisions’ adopted by the European Council (see Table 21.4). The EU Treaties can today be found on the European Union’s

EUR-Lex website: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/collection/eu-law/treaties.html, but there are also a number of solid paper copies such as Blackstone’s EU Treaties & Legislation or my own EU Treaties and Legislation collection. What is the structure of today’s EU Treaties? The structure of the TEU and TFEU is shown in Table 20.4. The (longer) TFEU is divided into ‘Parts’ – ‘Titles’ – ‘Chapters’ – ‘Sections’ –‘Articles’, while the (shorter) TEU only starts with a division into ‘Titles’. The EU Treaties are joined by numerous Protocols and the ‘Charter of Fundamental Rights’. According to Article 51 TEU, Protocols to the Treaties ‘shall form an integral part thereof’; and the best way to make sense of them is to see them as legally binding ‘footnotes’ to a particular article or section of the Treaties.
By contrast, the Charter is ‘external’ to the Treaties; yet it also has ‘the same legal value as the Treaties’.
How to Find (and Read) EU Secondary Law
The Union publishes all of its acts in the Official Journal of the European Union. Paper versions can be found in every library that houses a ‘European Documentation Centre’, but electronic versions are also openly available on the Union’s EUR-Lex website: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/oj/direct-access.html. The Union distinguishes between two Official Journal series: the L-series and the C-series. The former contains all legally binding acts adopted by the Union (including its international agreements), while the latter publishes all other information and notices. Originally, only the paper version of the Official Journal was ‘authentic’; but since 1 July 2013, electronic versions of the Official Journal (e-OJ) are equally authentic and therefore endowed with formal legal force.
Union secondary law will first mention the instrument in which it is adopted. It will typically have the form of a ‘Regulation’, a ‘Directive’ or a ‘Decision’. This will be followed by two figures. In the past, where the Union act was a regulation, the figure was: number/year; while for directives and decisions this was inversed: year/number. However, since 2015, this has changed and all main Union instruments are now arranged by year/number.treaty base would be complemented by a second treaty base in 1992, when the Maastricht Treaty created the (old) European Union.
Where the year and number are known for a given EU act, the easiest way to find it is to use the Union’s EU-lex search engine: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/homepage.html. Importantly, there may be two or more acts for a given number combination, especially where a ‘legislative’ act has been followed by a non-legislative act. For two types of non-legislative acts – namely: ‘delegated’ and ‘implementing’ acts – the EU Treaties require that they contain the word ‘delegated’ or ‘implementing’ in their title. This is to indicate – at first glance – that these executive acts have been adopted according to a particular decision-making procedure. States thereafter resorted to yet another ‘Amendment Treaty’: the 2007 Reform Treaty – also called the Lisbon Treaty.
What is the structure of a piece of Union legislation? After its ‘Title’ there follows a brief summary of the decision-making procedure that led to the adoption of the act – including a reference to the legal competence on which it was based. Thereafter comes the ‘Preamble’, which sets out the reasons for which the Union act has been adopted. The content of the act is subsequently set out in various ‘articles’, which may be grouped into ‘Sections’ and ‘Chapters’. For very technical Union legislation, there may also be an Annex – which, like a ‘Schedule’ in a UK statute, adds detailed provisions ‘outside’ the core content of the act. To illustrate this legislative structure, let us take a closer look at the Services Directive as it would be published in the Official Journal.

How to Find (and Read) EU Court Judgments
All EU cases are identified by a number/year figure. Cases before the Court of Justice are preceded by a C-, while cases decided before the General Court are preceded by a T-( for the French ‘Tribunal’).7 The Civil Service Tribunal prefixed its cases with an F-( for the French ‘Fonction publique’). Following this unique figure come the names of the parties to the case. A full case name would for example be: Case C-144/ 04, Werner Mangold v. Rüdiger Helm. However, since no one can remember all the numbers or all the parties, EU cases often get simply abbreviated by the main party; in our case Mangold.
In the past, judgments of all EU Courts were published in paper form in the purple-bound European Court Reports (ECR). Cases decided by the Court of Justice were published in the ECR-I series; cases decided by the General Court were published in the ECR-II series, while cases decided by the Civil Service Tribunal were published in the ECR-SC series. However, as of 2012, the entire Court of Justice of the European Union decided to go ‘paperless’ and it now publishes its judgments only electronically.8 The two principal websites here are the Court’s own curia website (http://curia.europa.eu/jcms/jcms/j_6), and the Union’s general EUR-Lex website (http://eur-lex.europa.eu/homepage.html). For the purposes of this book, the easiest way is however to go to www.schutze.eu, which contains all the judgments mentioned in the main text – including the ‘Lisbon’ version of all classic EU Court judgments.
Once upon a time, judgments issued by the European Court were – to paraphrase Hobbes –‘nasty, brutish and short’. Their shortness was partly due to a structural division the Court made between the ‘Issues of Fact and of Law’ (or later: ‘Report for the Hearing’), which set out the facts, procedure and the arguments of the parties, on the one hand, and the ‘Grounds of Judgment’ on the other. Only the latter constituted the judgment sensu stricto and was often very short indeed. For the Court originally followed the ‘French’ ideal of trying to put the entire judgment into a single ‘sentence’! A judgment like Van Gend en Loos contains about 2,000 words – not more than an undergraduate essay.



This world of short judgments is – sadly or not – gone. A typical judgment issued today will, on average, be four to five times as long as Van Gend. (And in the worst-case scenario, a judgment, especially in the area of EU competition law, may be as long as 100,000 words – a book of about 300 pages!) This new comprehensiveness is perhaps the product of a more refined textualist methodology, but it also results from a change in the organisation and style of judgments. Modern judgments have come to integrate much of the facts and the parties’ arguments into the main body of a ‘single’ judgment, and this has especially made many direct actions much longer and much more repetitive! The structure of a modern ECJ judgment given under the preliminary reference procedure may be studied by looking at Figure 20.2.
How to Find EU Academic Resources
The literature with regard to European Union law has exploded in the last 30 years. Today, there exists a forest of European law journals and generalist textbooks. Moreover, since the mid 1990s ‘European’ law has increasingly developed specialised branches that are sometimes even taught separately at university (as is the case at my own university). The three main branches here are: European constitutional law, European internal market law and European competition law. The first was explored in Parts I and II, while the second branch (and elements of the third branch) were covered in Part III. In addition to these three ‘bigger’ branches, the last two decades have also seen the emergence of many ‘smaller’ branches, such as European external relations law, European labour law and European environmental law. And there now also exist specialised LLM courses on EU consumer law and EU tax law.
The list of journals (Table 21.5) is by no means comprehensive. It is meant to point the interested reader to a first gateway for an in-depth study of a particular part of European Union law. My selection focuses primarily on English-language academic sources. But it goes without saying that European Union law is a ‘European’ subject with journals and textbooks in every language of the Union.

